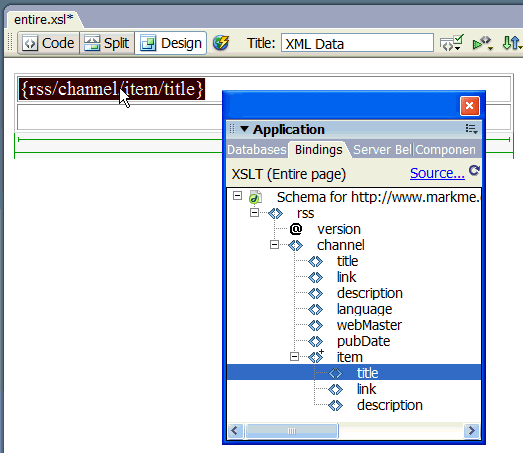
In the Bindings panel, select an XML element and drag
it to the place on the page where you want to insert data.
An XML data
placeholder appears on the page. The placeholder is highlighted and
in curly brackets. It uses the XPath (XML Path language) syntax
to describe the hierarchical structure of the XML schema. For example,
if you drag the child element title to the page, and that
element has the parent elements rss, channel, and item,
then the syntax for the dynamic content placeholder will be {rss/channel/item/title}.
Double-click
the XML data placeholder on the page to open the XPath Expression
Builder. The XPath Expression Builder lets you format selected data,
or select other items from the XML schema.